C if...else Statement
In programming, decision making is used to specify the order in which statements are executed. In this tutorial, you will learn to write if...else statements to make decisions in your program.
C if statement
The syntax of if statement is:
if (testExpression){// statement(s)}
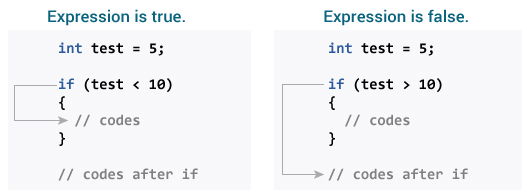
How if statement works?
The
if statement evaluates the test expression inside the parenthesis.- If the test expression is evaluated to true (nonzero), statement(s) inside the body of
ifis executed. - If the test expression is evaluated to false (0), statement(s) inside the body of
ifis skipped from execution.
To learn more on when test expression is evaluated to nonzero (true) and 0 (false), check relational and logical operators.
Example 1: if statement
// Program to display a number if user enters negative number#include <stdio.h>int main(){int number;printf("Enter an integer: ");scanf("%d", &number);// Test expression is true if number is less than 0if (number < 0){printf("You entered %d.\n", number);}printf("The if statement is easy.");return 0;}
Output 1
Enter an integer: -2 You entered -2. The if statement is easy.
When user enters -2, the test expression
(number < 0) is evaluated to true. Hence, You entered -2 is displayed on the screen.
Output 2
Enter an integer: 5 The if statement is easy.
When user enters 5, the test expression
(number < 0) is evaluated to false and the statement inside the body of if is skipped.C if...else statement
The
if statement may have an optional else block. The syntax of if..else statement is:if (testExpression) {
// statement(s) inside the body of if
}
else {
// statement(s) inside the body of else
}
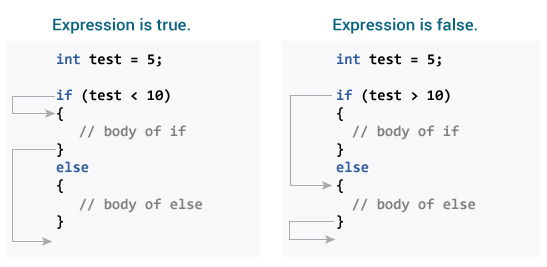
How if...else statement works?
If test expression is evaluated to true,
- statement(s) inside the body of
ifstatement is executed - statement(s) inside the body of
elsestatement is skipped from execution.
If test expression is evaluated to false,
- statement(s) inside the body of
elsestatement is executed - statement(s) inside the body of
ifstatement is skipped.
Example 2: if...else statement
// Program to check whether an integer entered by the user is odd or even#include <stdio.h>int main(){int number;printf("Enter an integer: ");scanf("%d",&number);// True if remainder is 0if( number%2 == 0 )printf("%d is an even integer.",number);elseprintf("%d is an odd integer.",number);return 0;}
Output
Enter an integer: 7 7 is an odd integer.
When user enters 7, the test expression
( number%2 == 0 ) is evaluated to false. Hence, the statement inside the body of else statement printf("%d is an odd integer"); is executed and the statement inside the body of if is skipped.if...else Ladder (if...else if....else Statement)
The
if...else statement executes two different codes depending upon whether the test expression is true or false. Sometimes, a choice has to be made from more than 2 possibilities.
The if...else ladder allows you to check for multiple test expressions and execute different statement(s).
Syntax of nested if...else statement.
if (testExpression1)
{
// statement(s)
}
else if(testExpression2)
{
// statement(s)
}
else if (testExpression 3)
{
// statement(s)
}
.
.
else
{
// statement(s)
}
Example 3: C if...else Ladder
// Program to relate two integers using =, > or <#include <stdio.h>int main(){int number1, number2;printf("Enter two integers: ");scanf("%d %d", &number1, &number2);//checks if two integers are equal.if(number1 == number2){printf("Result: %d = %d",number1,number2);}//checks if number1 is greater than number2.else if (number1 > number2){printf("Result: %d > %d", number1, number2);}// if both test expression is falseelse{printf("Result: %d < %d",number1, number2);}return 0;}
Output
Enter two integers: 12 23 Result: 12 < 23
Nested if...else
It is possible to include
if...else statement(s) inside the body of another if...elsestatement.
This program below relates two integers using either
<, > and = similar like in if...elseladder example. However, we will use nested if...else statement to solve this problem.Example 4: Nested if...else
#include <stdio.h>int main(){int number1, number2;printf("Enter two integers: ");scanf("%d %d", &number1, &number2);if (number1 >= number2){if (number1 == number2){printf("Result: %d = %d",number1,number2);}else{printf("Result: %d > %d", number1, number2);}}else{printf("Result: %d < %d",number1, number2);}return 0;}
If the body of
if...else statement has only one statement, you do not need to use parenthesis { }.
This code
if (a > b) {
print("Hello");
}
print("Hi");
is equivalent to
if (a > b)
print("Hello");
print("Hi");
Also Read: C switch statement
Comments
Post a Comment